DISCLAIMER: We are not financial advisors. The content or topic (Oil and Gas Leasing) on this website is for educational purposes only and merely cites our own personal opinions. In order to make the best financial decision that suits your own needs, you must conduct your own research and seek the advice of a licensed financial advisor if necessary. Know that all investments involve some form of risk and there is no guarantee that you will be successful in making, saving, or investing money; nor is there any guarantee that you won’t experience any loss when investing. Always remember to make smart decisions and do your own research!
Oil and Gas Leasing
In today’s economic landscape, many individuals and investors are seeking ways to generate passive income. Leasing oil and gas rights is a unique and potentially lucrative avenue for achieving this financial goal. With the increasing demand for energy resources, oil and gas leasing can offer a steady stream of income without the need for active involvement in day-to-day operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of leasing oil and gas for passive income. We will cover the basics, the benefits, the risks, and provide valuable tips and strategies to help you make informed decisions and maximize your earning potential in this dynamic industry.
Oil and Gas Leasing: Understanding
Leasing Oil and Gas involves landowners granting exploration and drilling rights to energy companies in exchange for royalties, lease payments, and bonus payments. These agreements allow energy companies to access and extract oil and gas resources from the landowner’s property.
The process typically starts with negotiation, followed by the signing of a lease agreement. The lease agreement outlines the terms, including the duration of the lease, royalty rates, bonus payments, and operational details.
Oil and Gas Leasing: Benefits
Leasing oil and gas rights can offer several compelling benefits, making it an attractive option for generating passive income:
Steady Income Stream:
It often provide consistent royalty payments, which can serve as a reliable source of passive income. This income stream can be particularly valuable for landowners who may not have other revenue sources from their property.
Portfolio Diversification:
Investors can diversify their portfolios by adding oil and gas leases, reducing their reliance on traditional investments like stocks and bonds. Diversification can help spread risk and enhance financial stability.
Capital Appreciation:
As energy resources are extracted from the leased property, the value of the land may appreciate over time, potentially leading to increased property value and profits upon selling or re-leasing.
Low Active Involvement of Oil and Gas Leasing:
It typically requires minimal day-to-day involvement, making it an ideal source of passive income. Landowners and investors can enjoy financial benefits without actively managing operations.
Inherent Demand:
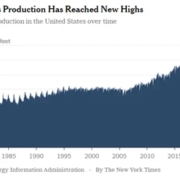
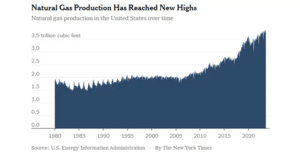
The global demand for energy resources, particularly oil and natural gas, remains consistently high. This demand ensures a continued market for oil and gas leases, creating opportunities for long-term income generation.
Oil and Gas Leasing: Risks and Challenges
While leasing oil and gas rights offers various benefits, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and challenges associated with this investment:
Market Volatility:
The oil and gas industry is known for its price volatility. Fluctuations in energy prices can affect the profitability of oil and gas leases and the income generated.
Environmental Concerns:
It can impact the environment, leading to potential regulatory changes and increased costs related to environmental compliance and remediation.
Regulatory Complexities:
Oil and gas leasing is subject to complex and evolving regulatory frameworks at the federal, state, and local levels. Staying compliant with these regulations can be a challenge.
Geopolitical Risks:
Global political events, trade tensions, and conflicts can influence the energy market, affecting the value and profitability of oil and gas leases.
Lease Performance Variability:
The actual performance of oil and gas leases can vary based on the property’s reserves, the technology used, and the energy company’s expertise.
Oil and Gas Leasing: Tips for Passive Income
To successfully lease oil and gas rights for passive income, consider these valuable tips:
Conduct Thorough Research
Before entering into any lease agreement, conduct comprehensive research. Assess the geological potential of the property, review historical production data, and identify any existing or potential environmental and regulatory challenges.
Seek Legal and Financial Guidance
Engage legal and financial professionals with expertise in oil and gas leasing. These experts can help you understand lease agreements, evaluate lease terms, and navigate the complex legal and tax aspects of the industry.
Negotiate Favorable Lease Terms
Negotiate lease terms that align with your financial goals. Ensure that royalty rates, bonus payments, and lease duration are favorable and competitive within the industry.
Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification can help spread risk. Consider including a mix of oil and gas leases in different regions or with different energy companies to reduce reliance on a single lease.
Monitor Market Trends
Stay informed about market trends, energy prices, and geopolitical events that could impact the industry. This information will help you make strategic decisions regarding your oil and gas leases.
Assess Environmental and Regulatory Factors
Be proactive in addressing environmental and regulatory challenges. Implement environmentally responsible practices, and stay compliant with evolving regulations to mitigate risks and potential liabilities.
Strategies for Maximizing Passive Income
To maximize passive income from oil and gas leasing, consider the following strategies:
Lease Structuring
Work with experienced professionals to structure your lease agreements in a way that optimizes income potential and minimizes risks.
Royalty Interest vs. Working Interest
Determine whether you prefer a royalty interest, where you receive a percentage of production revenue without operational responsibilities, or a working interest, where you have an ownership stake in the operations but also assume associated costs and risks.
Active vs. Passive Investment
Decide whether you want to actively manage your oil and gas leases or take a more passive approach. Passive investors may choose to work with reputable energy companies that handle day-to-day operations.
Tax Planning
Implement tax planning strategies to optimize your financial outcomes. Consult with tax professionals who understand the unique tax implications of oil and gas leasing.

Oil and Gas Leasing rights for passive income is a compelling financial opportunity for landowners and investors. With the potential for steady income streams, capital appreciation, and portfolio diversification, oil and gas leases can be a valuable addition to your investment strategy.
However, it’s essential to approach this industry with careful consideration, thorough research, and the guidance of legal and financial experts. By staying informed about market trends, understanding the challenges and risks, and employing strategic leasing and investment approaches, you can harness the passive income potential of oil and gas leasing while mitigating potential pitfalls. Remember that the world of oil and gas leasing is dynamic, and proactive management is key to long-term success in this field.
If you have further questions related to the topic, feel free to reach out to us here.